How convincing is a crowd? Quantifying the persuasiveness of a consensus for different individuals and types of claims
Abstract
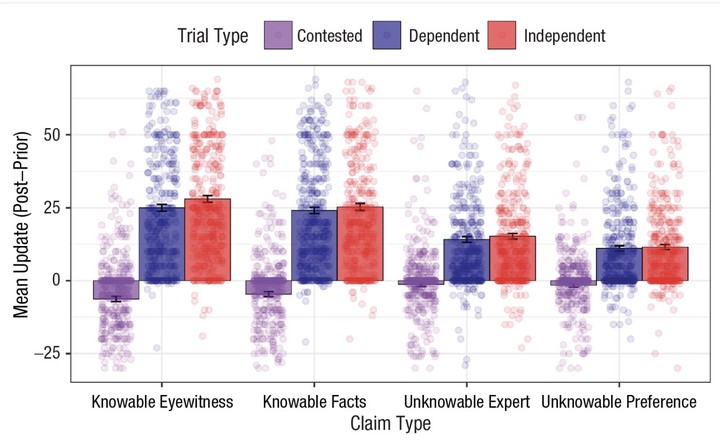
A powerful cue when reasoning is whether an apparent consensus has been reached. However, we do not yet know how the strength of this cue varies between different individuals and types of claims. In the current study (N = 78 U.S. adults, recruited from Prolific), we evaluated this with a realistic mock social-media paradigm in which each participant evaluated 60 diverse, real-world claims based on posts from people who either disagreed with each other, formed a consensus independently, or formed a consensus using shared sources. Almost all participants revised their beliefs to align with the consensus; many also qualitatively changed their minds. A consensus was also more persuasive for claims more likely to have a ground truth (i.e., more knowable claims). Although most people were insensitive to consensus independence, some were more persuaded by a consensus formed independently, whereas some were equally convinced by a consensus formed using the same sources.